The successful performance of university scientists at the conference «2025 IEEE 6th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology» is the result of active cooperation and partnership between faculties and scientific institutions

On October 06-10, 2025, Kharkiv Polytechnic University hosted the 6th International Conference «2025 IEEE 6th KhPI Week on Advanced Technology», organized by the international organization IEEE — «the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity».
The IEEE has more than 600,000 members from more than 160 countries around the world, and 45 of which are located in the United States of America, and brings together engineers, scientists and manufacturers in the fields of electronics engineering, electrical engineering, computer science, various modern technologies, nanotechnology and other related fields.

At the current conference, 6 tracks were presented, namely: Power Electronics, Industrial Electronics, Power & Energy Systems, Computer Sciences, Micro-& Nanotechnology, Computational Intelligence (electronics, electrical materials, computer science, power and energy systems, micro and nano-materials, engineering in biology and medicine, management in technology and engineering) more than 150 participants presented their scientific achievements. The working language of the conference is English.

Two joint studies of our scientists from the faculties of information technology and construction and design were presented on the second day of the conference and aroused great interest among the participants of this important scientific event.
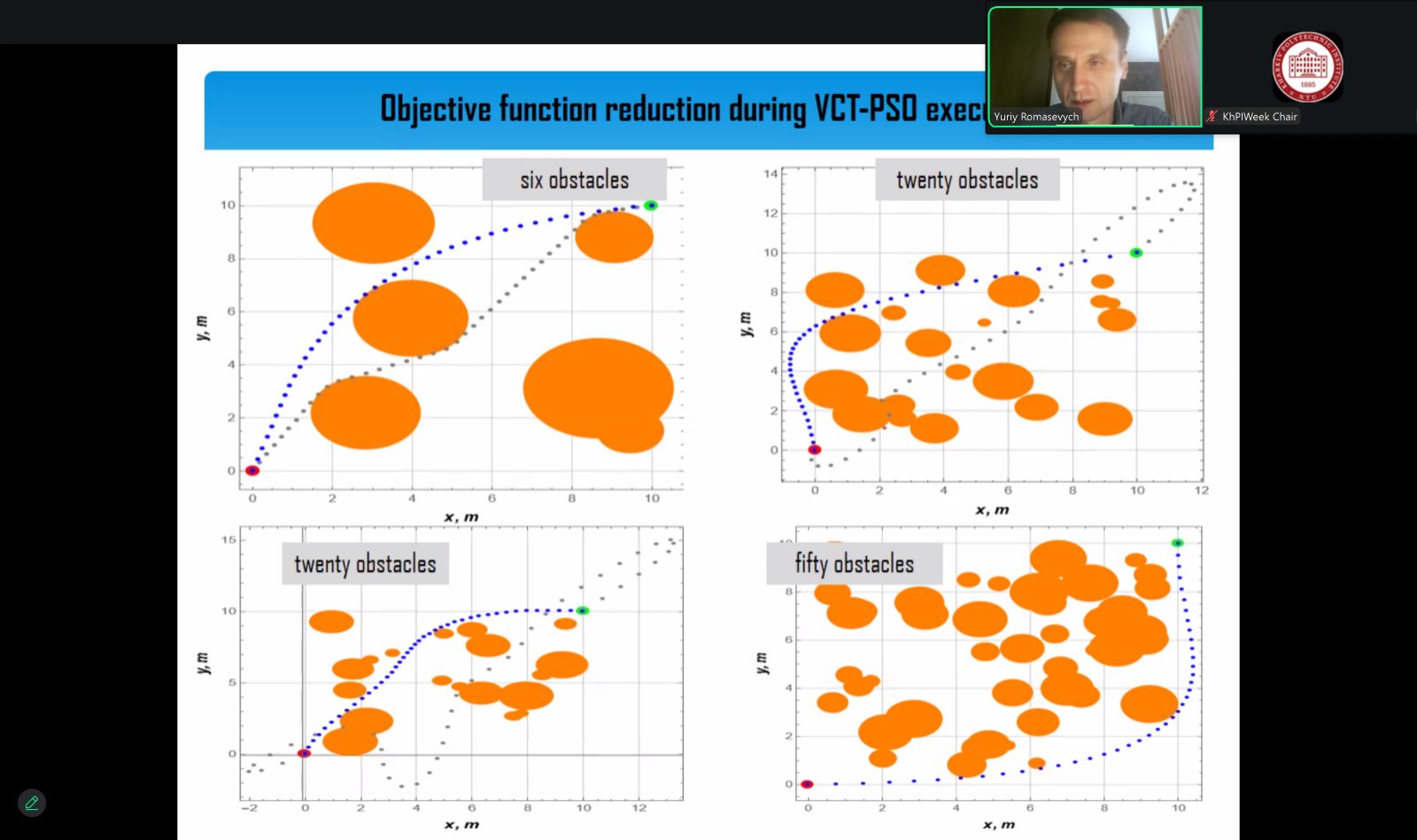
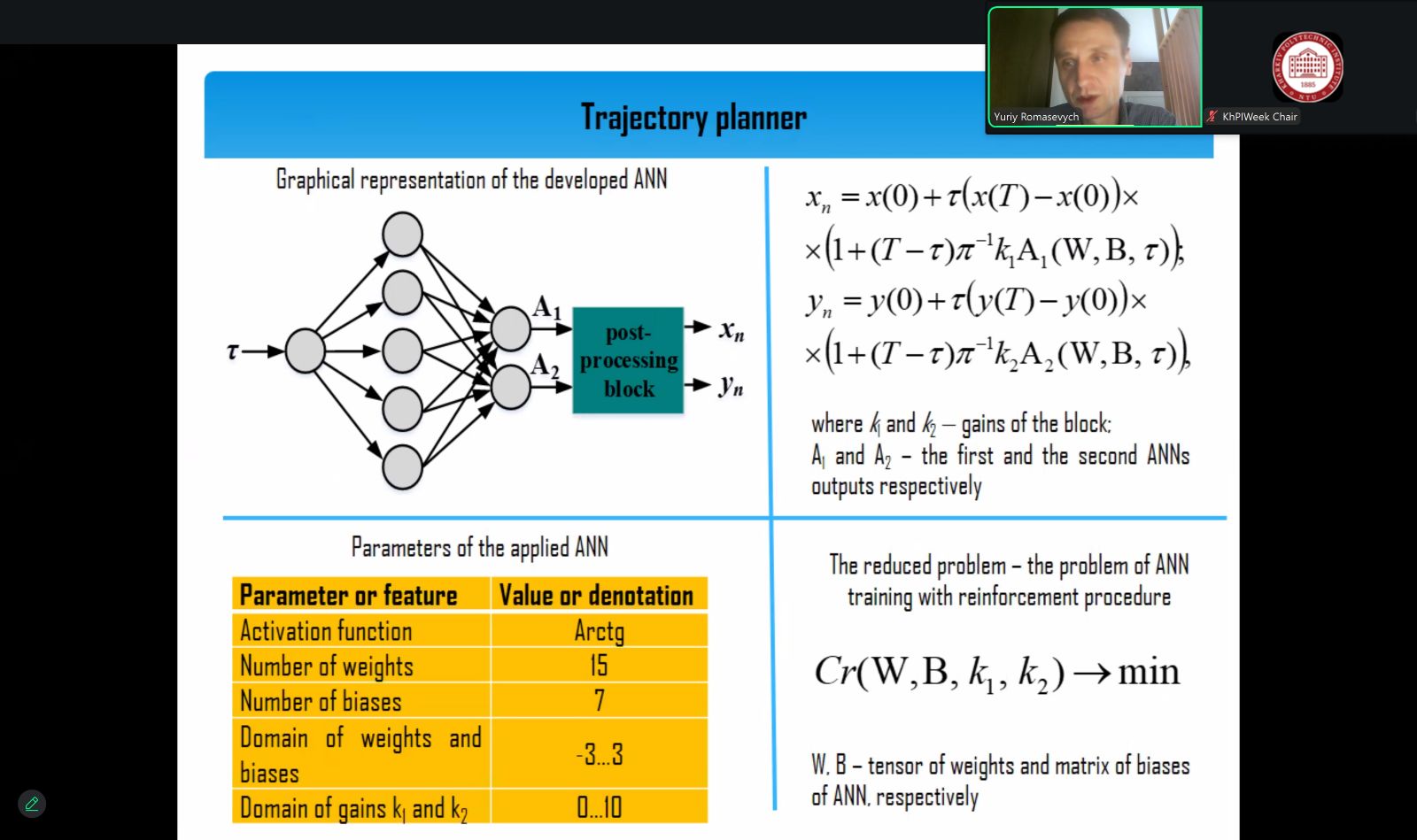
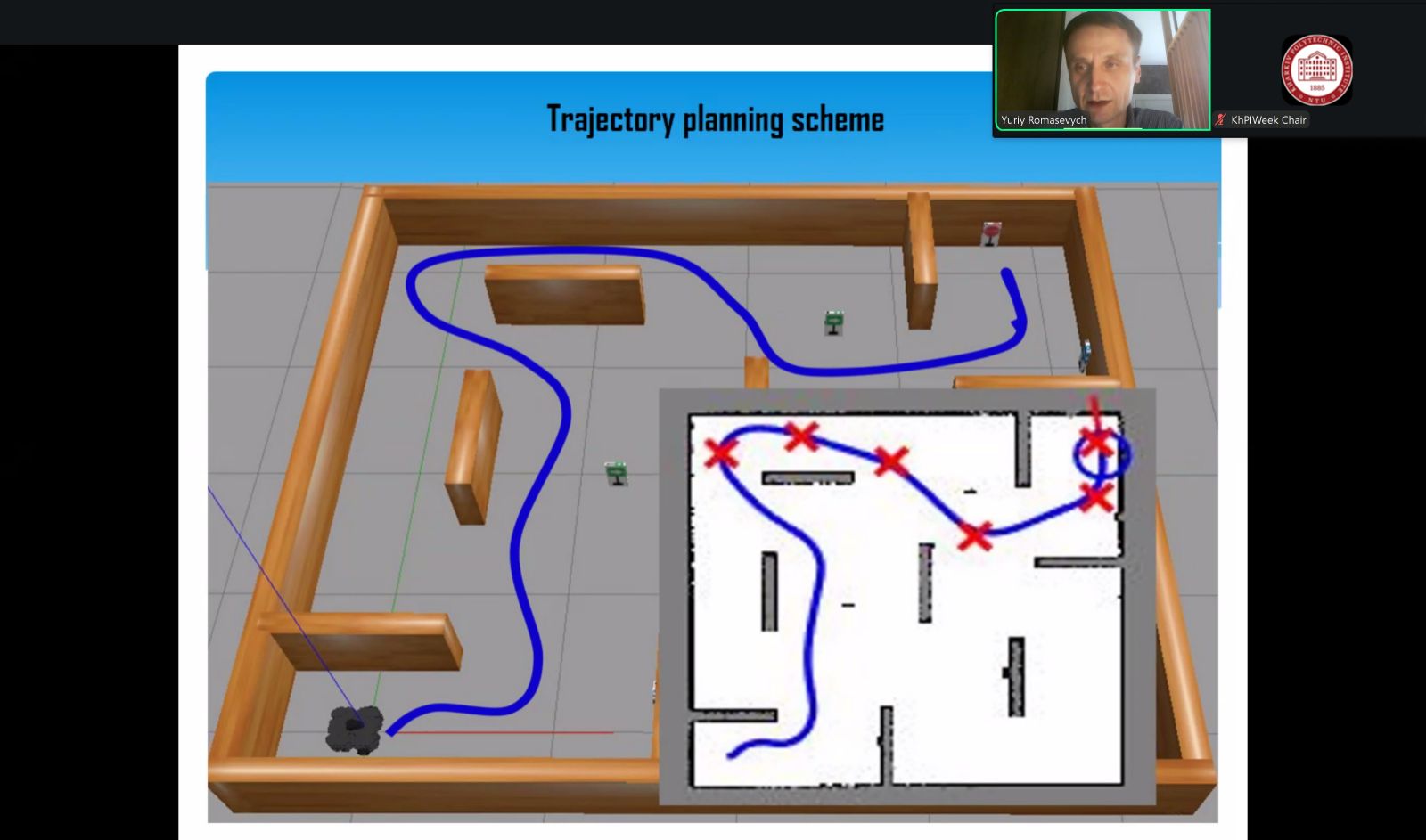
So, Yuri ROMASEVYCH, professor of the department of engineering and equipment design and Volodymyr NAZARENKO, associate professor of the department of computer systems. networks and cybersecurity made a presentation «Optimal Robot Trajectory Planning via Artificial Neural Network Reinforcement Learning with Metaheuristic Optimizer». Their report was devoted to solving the problem of planning the trajectory of a mobile robot in an environment with obstacles.


The authors set an optimization problem-it was necessary to get a trajectory of the minimum length. To solve this problem, an intelligent trajectory planner — an artificial neural network (ANN) — was used. The initial problem was reduced to the problem of minimization without restrictions and formulated in terms of training the ANN according to the "with reinforcement" paradigm. To solve the problem, a modified VCT-PSO particle swarm method was used, which allowed us to obtain the ANN parameters. The method of solving the problem was tested for robot motion environments with 6, 12, and 50 obstacles. For all motion scenarios, the ANN allowed to obtain the desired optimal trajectory.
Report on the topic «Synthesis, Structural Characteristics, and Phase Transformations of Iron-Based Nanoparticles Obtained by Electric Spark Treatment and Their Application in Steel Modification» made by Kostyantyn LOPATKO, head of the department of structural materials technology and materials science (SMTMS), Oksana ZAZYMKO, associate professor of the department of structural materials technology and materials science, Volodymyr NAZARENKO, associate professor of the department of computer systems, networks and cybersecurity and Evhen AFTANDILYANTS, head of the laboratory of the Institute of physics and technology of metals and alloys of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine.
The report was presented by Volodymyr Anatoliyovych, who informed the conference participants about the features of electric spark dispersion of conductive materials in a liquid, which consists in obtaining an ultrafine state of matter, as well as about the possibilities of computer modeling of such processes.


Thanks to the experiment conducted, this study demonstrated that electric spark treatment of iron granules in liquid media is an effective and controlled method for synthesizing iron-based nano-particles with individual size distribution, phase composition, and Lattice characteristics. The authors performed complex structural and thermodynamic characterization using scanning electron microscopy (Jeol-6490lv, Jeol JSM6360, Hitachi SU8000 SC200D), X-ray diffraction (emission DRON-UM1, Cu Ka), x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ES-2401), and synchronous thermal analysis (STA 449 F1).
The practical applicability of nano-particles as modifiers of the microstructure of steel was confirmed by quantitative metallographic analysis of 45L steel. It was found that the addition of nano-particles increases the content of perlite in the cast state by 16%, and after annealing at 860 °C — by 42%, refined ferrite grain size — up to 2.4 times, reduces the grain size of perlite — up to 1.5 times, increases structural uniformity up to 2.4 times.


In general, the results obtained by the authors provide evidence that iron nanoparticles synthesized by an electric spark have unique structural and phase transformation properties that are directly responsible for significantly improving the microstructure of steel. The results obtained can be independently verified and applied to modern metallurgical production of alloys and materials science.
Further joint developments of the authors will be aimed at conducting computer modeling of the studied processes and building computer vision models for analyzing images of the results obtained.
Employees of the department of computer systems, networks and cybersecurity of the faculty of information technologies and departments of machine and equipment design and TCM and MS of the faculty of construction and design are planning to further expand scientific ties with various departments of the University and scientific institutions.